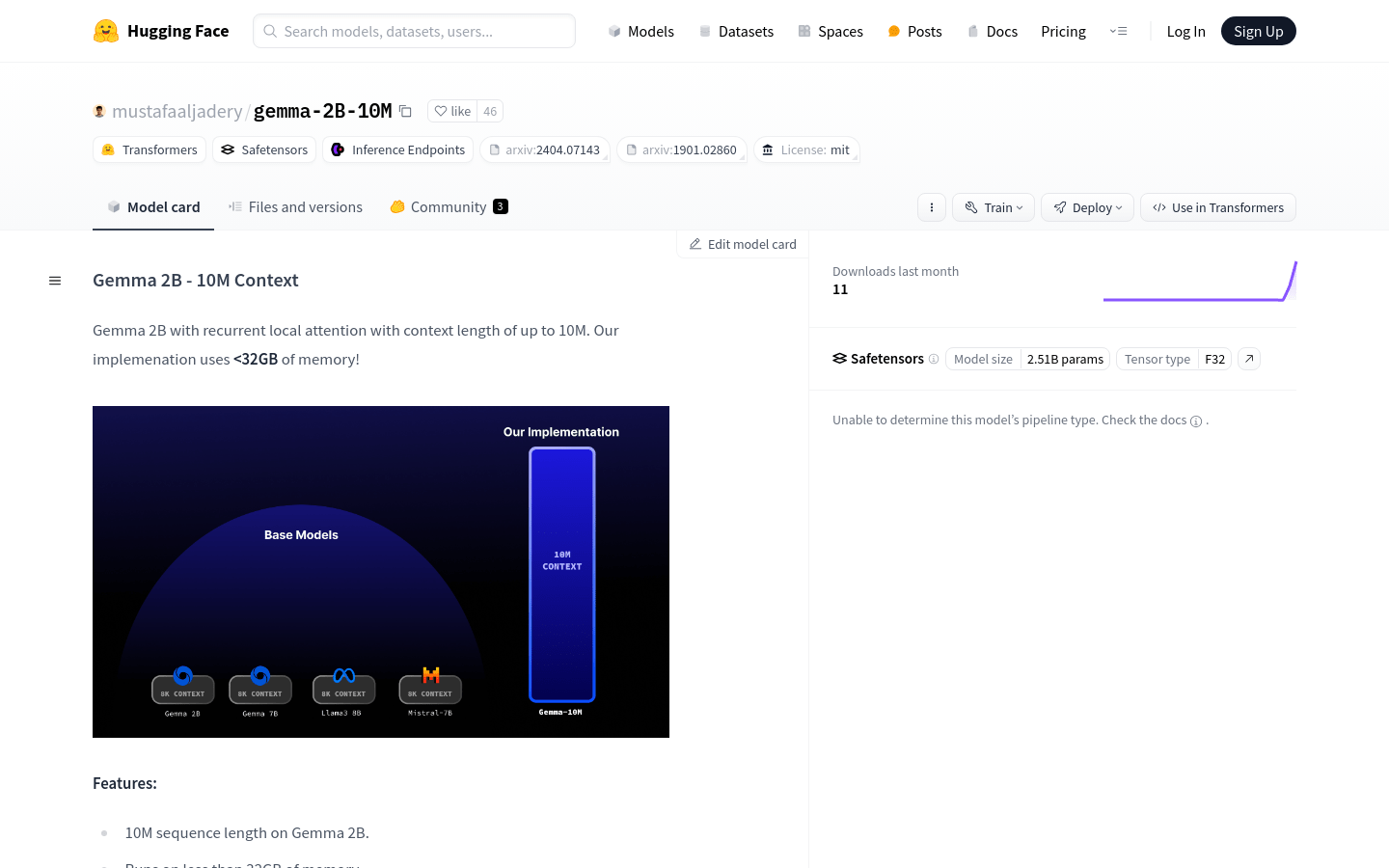
💻
programming Category
AI model inference training
Found 53 AI tools
53
tools
Primary Category: programming
Subcategory: AI model inference training
Found 53 matching tools
Related AI Tools
Click any tool to view details
Related Subcategories
Explore other subcategories under programming Other Categories
💻
Explore More programming Tools
AI model inference training Hot programming is a popular subcategory under 53 quality AI tools